
It is, therefore, concluded that both long-range exchange interactions and dispersion correlations are essentially required in conventional functionals to investigate Diels-Alder reactions quantitatively. Consequently, we found that dispersion correlation correction is also crucial to give accurate barrier height energies. The barrier height energies were also computed for these reactions. As a result, it is found that the long-range correction drastically improves the reaction enthalpies. First, we calculated the Diels-Alder reaction enthalpies that have been poorly given by conventional functionals including B3LYP functional.

this allows good electron flow from the diene HOMO to the alkene LUMO.the reaction goes best with alkenes having electron-withdrawing substituents (dienophiles).cyclopentadiene undergoes reaction with itself.cyclic dienes are much more reactive than acyclic dienes.s-cis means the single bond between the two double bonds is cis.the diene must be in an s-cis conformation for this reaction.such transition states are particularly stable when they have (4n+2) electrons.note that the transition state is a 6-membered ring of delocalized pi electrons.overall, two pi bonds are converted to two sigma bonds while making the ring.cycloaddition of a diene to an alkene (usually called a dienophile in this reaction).in most situations, a more stable product means a lower barrier (The Hammond Postulate).Note - this situation of the more stable product having a higher activation barrier is unusual.thermodynamic control requires equilibration to form the more stable product, since it has a higher barrier.thermodynamic control - the more substituted alkene is the more stable product.kinetic control (lower Ea) - the more substituted cation has more + charge, reacts faster.heating the kinetic mixture of products gives the thermodynamic mixture (i.e., mostly 1,4).addition at high temperature favors the 1,4-addition product (thermodynamically controlled).addition at low temperature favors the 1,2-addition product (kinetically controlled).the two ends of the allyl cation may be nonequivalent.conjugated dienes can give 1,2 or 1,4 addition.addition gives a relatively stable allylic cation.conjugated dienes are very reactive towards electrophiles.frontier MOs are the most important for electron pushing.1,3-butadiene - 4 pi MOs (two bonding and two antibonding) with 4 pi electrons.allyl cation (2 pi electrons), allyl radical (3 pi electrons), allyl anion (4 pi electrons).allyl pi system (could be cation, radical, or anion) - 3 pi MOs (bonding, nonbonding, antibonding).ethene - pi bond and pi* antibond, with two electrons in the pi bond.
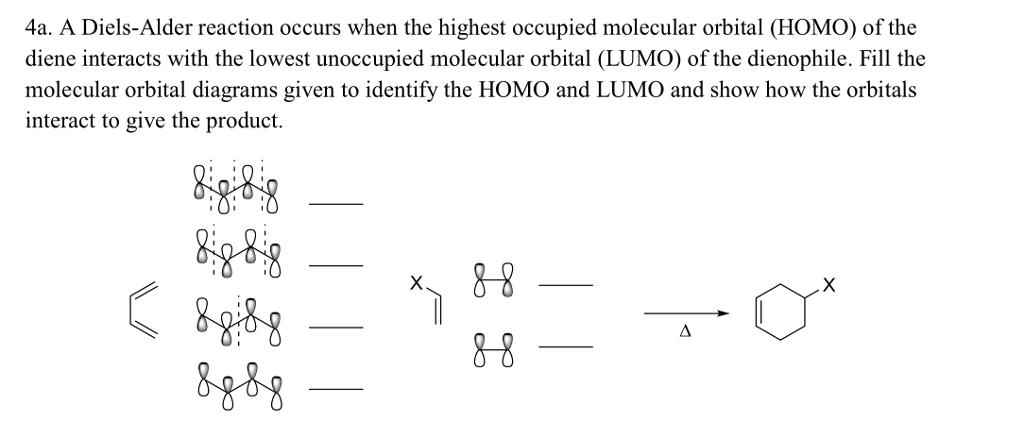
n atomic orbitals (AOs) combine to make n molecular orbitals (MOs).Molecular Orbitals (MOs) of Conjugated Pi Systems Chem 336 - Spring 1999 - Organic ChemistryIII


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
